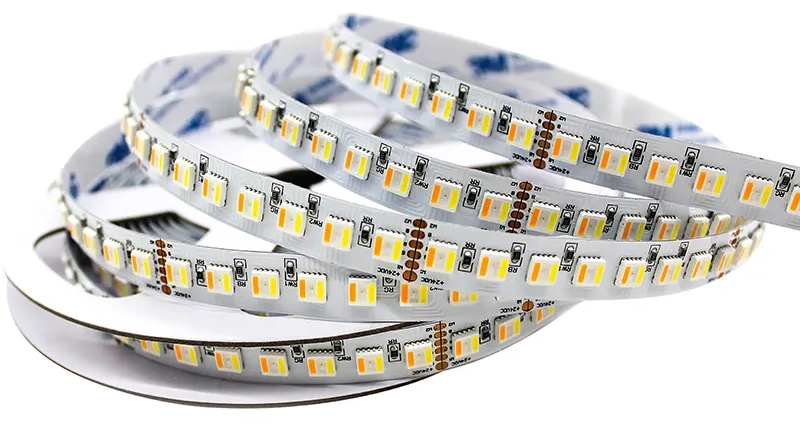
Many individuals consider toupee and hair system options for hair loss. Some use these two solutions interchangeably, but they differ in aesthetics, durability, and application methods to meet different needs. Understanding the differences between toupees and custom hair systems is crucial. Their natural appearance, attachment methods, longevity, and cost are examined. Shunfa Hair aim to help you make an informed decision that fits your lifestyle and hair loss solutions goals as we explore non-surgical hair replacement, synthetic and real hair options, and innovative hair integration systems.
What are Toupees and Hair Systems?
Toupees and hair system are popular solutions for individuals who want to address hair loss, but they serve different needs. A toupee is a small hair piece or partial wig made of natural or synthetic hair that covers bald spots. Men seeking a simple, temporary solution to hair loss have traditionally used toupees. They fit snugly over the problem area and blend with the wearer’s hair.
A hair system is a more advanced and comprehensive non-surgical hair replacement method. In contrast to toupees, system hair prostheses can range from small pieces to a full scalp prosthesis, providing solutions for varying degrees of hair loss. Hair systems are customised to match the wearer’s hair colour, texture, and style for a natural look. These systems are attached to the scalp with special adhesives for a secure, daily-wear fit.
From toupees to undetectable, long-lasting hair systems, non-surgical hair replacement has advanced greatly. Individuals can now have full heads of hair without surgery thanks to advancements in materials and attachment methods. Individuals now have access to hair loss solutions that can be tailored to their unique needs, ensuring confidence and comfort, whether they choose men’s toupees or custom hair systems.
Differences between a toupee and a hair system
Knowing the differences between a toupee and a hair system is essential when researching hair loss solutions. Coverage area is a major difference. A toupee is suitable for partial hair loss because it covers only specific bald spots or thinning areas. Individuals with extensive hair loss can use hair systems, which offer a wider range of coverage options, from partial to full scalp.
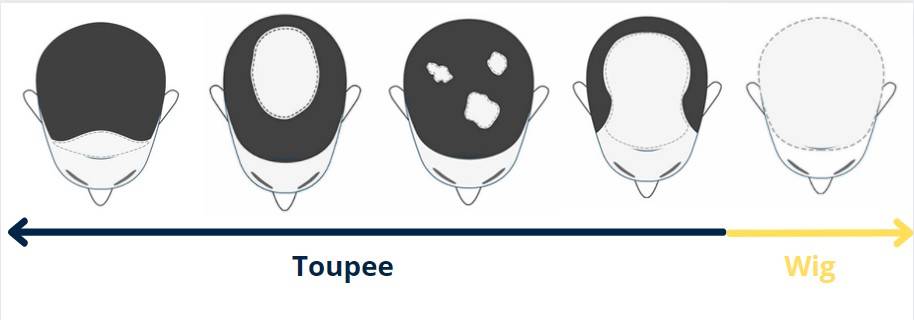
The materials used in both options also affect their appearance and feel. Long-term hair replacement with synthetic hair systems is affordable due to their durability and ease of maintenance. Real hair toupees mimic the wearer’s natural hair and allow for more styling flexibility.
The two differ further in customisation and fitting. Custom hair systems blend seamlessly with natural hair by accommodating the wearer’s scalp contours and hair colour, density, and texture. This customisation guarantees a comfortable fit and natural look. While available in various sizes and styles, standard toupees may not offer as much personalisation, resulting in a less natural look and feel.
Natural Look and Durability
In hair loss solutions, naturalness is key. This makes many wonder if toupees look natural like hair systems. Answer depends on hairpiece quality and customisation. Advanced technology and bespoke fitting allow hair systems to blend seamlessly with the wearer’s hair, creating a natural, undetectable look. To ensure a perfect fit, they match the wearer’s hair colour, density, texture, and scalp shape.
However, toupees have improved and can look natural when made of high-quality materials and fitted properly. Hair system customisation and coverage options give them an edge in achieving a more natural look.
Hair systems lead the way in durability. Carefully maintained hair systems can last months due to their durable materials and daily wear. Whether a hair system is made of synthetic or real hair affects its longevity. Real hair requires more maintenance but looks and feels more natural. Due to less advanced attachment methods and materials, toupees may last less and require more frequent replacements.
Both toupees and hair systems can help people with hair loss, depending on their needs for natural appearance and durability.
Attachment Methods
Wearers of toupees and hair systems feel secure and confident in their daily lives thanks to improved attachment methods. Toupees are attached with double-sided tape or liquid adhesives. Tape or adhesive is applied to the toupee base and carefully placed on the scalp. This method requires precise application for a natural look and secure fit. To keep the toupee in place, reapply the adhesive or tape regularly.
However, hair systems use advanced techniques for permanent results. Bonding uses a medical-grade adhesive to attach the hair system to the scalp for weeks. This method creates a strong, undetectable bond for high activity without displacement. Another method is weaving or sewing the hair system into the wearer’s hair, which provides more security but requires adjustment as natural hair grows.
Scalp prosthesis is a key component of hair integration systems. This prosthesis is specifically designed to fit the wearer’s scalp, which has hair. Special adhesives attach the prosthesis to the scalp for a secure, natural-looking solution. This method provides full coverage and a seamless appearance, making it ideal for individuals who have experienced significant hair loss.
Each attachment method has advantages for different needs and preferences. Individuals can benefit from a secure, natural-looking hair replacement solution that improves their appearance and confidence, whether they choose to wear a toupee temporarily or a hair system or scalp prosthesis more permanently.
Concerns about cost
Cost is a factor for many individuals when considering hair loss solutions. The materials, customisation, and attachment method make toupees and hair systems very different in price. Toupees cost less than hair systems upfront. This is because toupees use simpler materials and technologies and offer fewer customisation options. Their partial coverage design lowers their initial cost.
Hair systems require a larger initial investment. This is due to the high-quality real or synthetic hair, advanced technology, and personalised fitting and styling. Hair systems are seamless and natural because they match the wearer’s hair colour, density, texture, and scalp shape. The complicated process of designing and fitting a custom hair system raises its price.
However, cost must include long-term investments as well as initial costs. While cheaper at first, toupees may require more frequent replacements and maintenance, which can add up. With proper care, hair systems last longer and may be more cost-effective. A hair system may be more affordable over time for some individuals due to its durability and longevity, which can offset its higher initial cost.
A toupee or hair system should be chosen based on cost, lifespan, maintenance, and the value of a natural, confidence-boosting appearance. Individuals can make the best decision for their needs and budget by carefully weighing these factors.
Selecting Your Solution
The right hair loss solution depends on many factors, each of which is important for an individual’s needs. When choosing between a toupee and a hair system, lifestyle, hair loss, and budget all affect effectiveness and satisfaction.
Lifestyle is important; for individuals with active or physically demanding lives, a hair system may be preferable. Advanced attachment methods in these systems provide peace of mind and confidence during rigorous activities. However, toupees may be better for those seeking a less permanent option with more removal and maintenance options.
Another important factor is hair loss severity. Male toupees are designed for partial hair loss, such as crown thinning or receding hairlines, and may not suit extensive hair loss. Hair systems, such as scalp prosthesis and hair integration systems, can treat hair loss from complete baldness to varying degrees, so there’s a solution for almost every situation.
No budget should be ignored. High-quality toupees may cost less initially, but replacements and maintenance can be costly. Due to their customisation and durability, hair systems may cost more initially, but they may save money over time due to longevity and fewer replacements.
These factors, along with the desired appearance and how each option fits with aesthetic goals, must be considered when personalising your hair loss solution. Selecting men’s toupees for subtle enhancements or advanced hair integration systems for comprehensive coverage should support the wearer’s comfort, confidence, and lifestyle.




