Pumps are one of the most common pieces of equipment used in industrial and commercial settings. They’re responsible for moving fluid from one place to another – whether that’s in a water pipeline, a manufacturing plant, or an oil refinery.
As pumps become more and more efficient, it’s important to understand how pump efficiency changes with speed. In this article, we’ll explore this topic by looking at some experiments conducted on pumps.
First, let’s take a look at what happens to the efficiency of a pump when it’s moving at different speeds. A study conducted by the University of Illinois found that the efficiency of a pumped water system drops by around 10% as the speed of the pump increases. This is due to the fact that higher speeds cause turbulence in the fluid being pumped, which results in decreased flow rates.
Interestingly, this decrease in efficiency isn’t uniform – it varies depending on the type of pump being used. For example, centrifugal pumps are more efficient than axial pumps at lower speeds, but become less efficient as speed increases. This is because centrifugal pumps use a rotating impeller to create pressure differences within the fluid, while axial pumps rely on direct contact between the pump and the fluid.
Overall, these findings suggest that it’s important to choose a speed for your pump that suits its specific design characteristics. If you’re using an inefficient pump, increasing speed will only make matters worse.
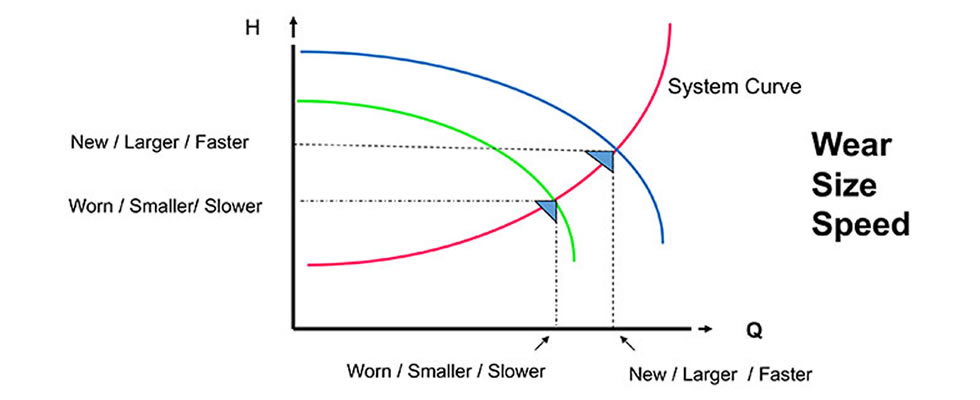
What is a pump?
Pumps are devices that transfer water, oil, gas, or other fluid substances between two points. In most cases, pumps are used to move large amounts of material at a high speed. However, pump efficiency does not change with speed.
Pump efficiency is the percentage of energy that is transferred from the input to the output of a device. The higher the efficiency, the more energy is transferred per unit of work done. Pump efficiency changes with speed because as the speed of the pump increases, so does the amount of turbulence in the fluid being moved. This turbulence causes more energy to be wasted in heat than is actually transferred to the output.
What is a good pump for different types of equipment?
When shopping for a pump, it is important to consider the application. There are different types of pumps designed for specific needs. For example, a reciprocating pump is often used in agricultural settings to move water or oil, while a centrifugal pump is more commonly found in manufacturing and processing applications. The type of pump also affects how efficiently it works. For example, a reciprocating pump will work more efficiently if it is running at lower speeds, while a centrifugal pump will work better at higher speeds. It is important to match the speed of the pump to the application so that the equipment can operate at its maximum potential.
There are also different types of pumps available with specific features. For example, some pumps have a discharge hose that is adjustable, while others do not. This can be important if the pump must work in close quarters or if it must move large amounts of material. Some pumps also come with a built-in sensor that controls the speed of the pump based on the amount of material being moved.
What is Pump Efficiency?
Pump efficiency is the percentage of energy that is converted into work by a pump. The higher the pump efficiency, the more energy that is used to move water through the system. This can be important when calculating water usage or when choosing a pump for a specific application.
Pump efficiency can also be affected by a number of factors, including the type of pump, the size and configuration of the system, and the quality of the water.
The pump efficiency of a water system can be affected by a number of factors, including the type of pump, the size and configuration of the system, and the quality of the water.
Does it change with speed?
The pump efficiency of a centrifugal pump is affected by the speed at which the impeller is rotation. Pump efficiencies are typically higher when pumps are rotating slowly, and lower when pumps are rotating faster. This can be attributed to the fact that as the speed of the impeller increases, there is less time for the fluid to be transferred through the impeller. Additionally, as the speed of the impeller increases, there is also a greater chance that cavitation will occur, which can decrease pump efficiency.
Generally, pump efficiencies are highest when pumps are rotating slowly, and decrease as the speed of the impeller increases.
Is pump efficiency affected by speed?
pumps are often used in conjunction with valves to control water flow. When a pump is operating at high speed, it can expend more energy than when it is operating at a lower speed. It has been theorized that this difference in energy expenditure results in a difference in pump efficiency. However, recent studies have failed to support this claim.
A study published in the Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management looked at pump efficiencies for both slow and fast pumps over a range of speeds. The study found no significant difference between the efficiencies of slow and fast pumps at different speeds. Furthermore, the study found that pump efficiencies actually decreased as speed increased, due to the increased energy expenditure. This suggests that higher speeds may actually result in lower water production rates.
The reason for this discrepancy between theory and reality may be due to the way pumps are designed. Slow pumps are typically designed with a higher flow rate than fast pumps, which allows them to operate at a slower speed without losing efficiency. Fast pumps, on the other hand, are typically designed with a lower flow rate, which results in an increased energy expenditure when they are operated at high speeds.
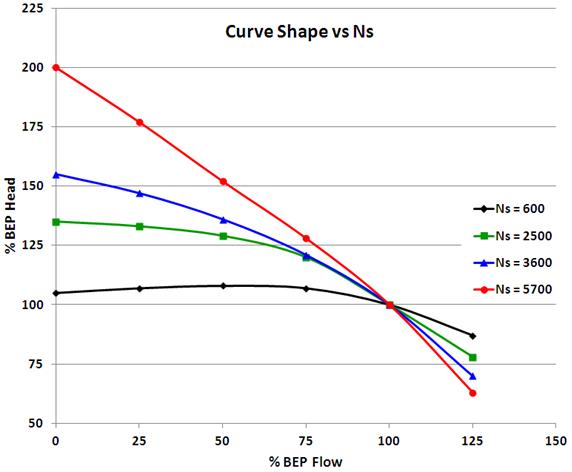
Do Other Variables Affect Pump Efficiency?
Pump efficiency is a critical parameter in controlling fluid flow and is affected by a variety of variables. Pump efficiency can be greatly improved by increasing the speed at which the pump operates, but other factors must be considered when optimizing pump performance.
Pump size, impeller type, and flow rate are all important factors that affect pump efficiency. Additionally, the type of fluid being pumped can also have a significant impact on pump efficiency. For example, a pump designed to move a viscous liquid may be less efficient than one designed to move a gas.
Is there a difference in pump efficiency with different speeds?
There is some debate over the effect of speed on pump efficiency and while there is no definitive answer, there are a few things to consider.
When a pump is moving fluid through it, the impeller creates a rotating force that converts energy into motion. The faster the impeller spins, the more energy is converted into motion and the greater the pump’s efficiency. However, too much speed can also cause problems like cavitation which can damage the pump or even cause it to fail.
Generally speaking, pumps operate at a certain speed based on their design and intended use. For example, centrifugal pumps typically operate at high speeds to handle large volumes of liquid, while water pumps are usually designed for lower speeds to reduce noise and vibration. It’s important to keep in mind that this speed is always dependent on the particular pump and its environment – if you want to increase efficiency, you’ll need to find a different speed that works best for your application.
Conclusion
Yes, pump efficiency does change with speed. When the flow rate is increased, the pump becomes less efficient and requires more power to do the same job. This can lead to higher energy costs and decreased performance.
It is important to match the speed of the pump to the application so that the equipment can operate at its maximum potential. When choosing a pump, it is also important to consider the size and configuration of the system, as well as the quality of the water being transferred.
Does pump efficiency change with speed,please click topkitparts see more
