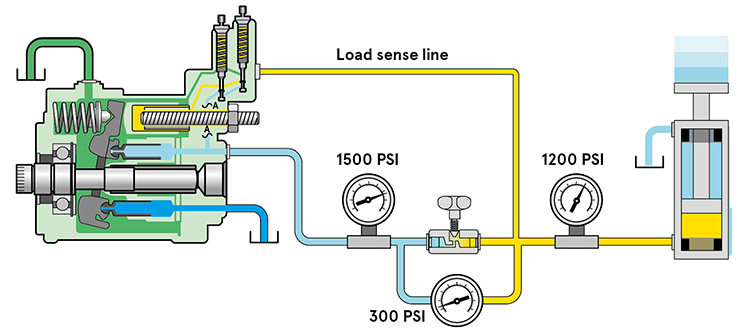
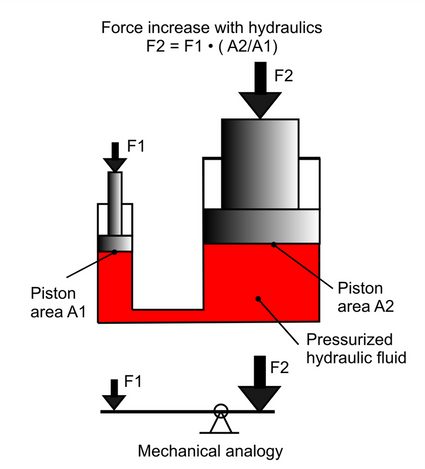
Hydraulic pumps are essential in many industrial and commercial applications, powering everything from cars to factories. But how do you keep one running smoothly? In this article, we’ll explore the basics of hydraulic pump maintenance, including troubleshooting procedures and tips for keeping your machine running at its best.
What is a hydraulic pump?
A hydraulic pump is a machine that uses pressurized fluids to move objects. Hydraulic pumps are found in a variety of applications, including construction, mining, agricultural, and industrial sectors.
Maintaining a hydraulic pump can be a challenge. Proper care and maintenance can help ensure the pump is functioning properly and reducing the risk of failure.
Here are some tips on how to maintain a hydraulic pump:
1. Keep the area around the pump clean. Dirty areas can cause the pump to work harder and create more wear and tear on it. Cleaning the area around the pump can help reduce this wear and tear.
2. Check the fluid level and replace any lost or damaged fluid containers as needed. Fluid levels should be checked regularly to make sure they are at their desired level and that there are no leaks present. If there are leaks, they should be repaired as soon as possible to avoid damage to the pump or surrounding areas.
3. Inspect the seals and other components of the pump regularly for signs of wear or damage. If there are any signs of deterioration, replace these components as soon as possible to avoid major damage or failure of the pump.
4.Regularly lubricate all moving

Basics of a Hydraulic Pump
Maintaining a hydraulic pump can be a daunting task, but with the right tools and techniques, it can be done easily. Here are some basics to keep in mind:
– Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for care and use.
– Inspect the pump regularly for wear, damage, and leaks.
– Keep the oil level high and clean the pump regularly.
– Drain and clean the reservoir if necessary.
How do they work?
Hydraulic pumps are one of the most important mechanisms used in modern industrial and commercial applications. They are often used in a variety of settings, including mining, wastewater treatment, oil and gas production, and manufacturing. When you start working with hydraulic pumps, it’s important to understand how they work and how to maintain them.
Hydraulic pumps use pressurized fluid to move objects or fluids. They operate using two basic principles: the suction pump principle and the displacement pump principle. The suction pump principle uses a cylinder filled with pressurized fluid to suck items or liquids up from a lower level to a higher level. The displacement pump principle uses a piston that moves up and down inside a cylinder filled with pressurized fluid. This movement creates a flow of liquid or objects up and down the pipe.
There are many different types of hydraulic pumps, but all of them use these same two basic principles to move things or fluids. To keep your hydraulic pump running smoothly, it’s important to keep these principles in mind:
1) Always make sure that the cylinder is full of pressurized fluid. Overfilling the cylinder can cause the pump to malfunction.
2) Make sure that
Why is it important to maintain a hydraulic pump?
Hydraulic pumps are one of the most important pieces of equipment on a farm. Without them, many of the tasks we take for granted would be incredibly difficult or impossible to do. A hydraulic pump is essentially a device that uses pressurized fluid to move objects or fluids. They’re used in everything from irrigation systems to cropdusting planes, and they play an essential role in all sorts of farming activities.
Why is it so important to keep a hydraulic pump running smooth and efficient?
There are a few reasons. First of all, a malfunctioning pump can quickly become a costly problem. For example, if your irrigation system is not working properly, you’re going to have to water your crops using groundwater instead. This will obviously take much longer than simply pumping water directly from the river or lake where your farm sits. In addition, small problems can quickly snowball into bigger ones if they aren’t addressed promptly. For example, if your hydraulic pump is failing to raise water levels high enough in your irrigation system, it will eventually start sucking water out of lower levels, leading to flooded fields and lost crops. Finally, there’s just something really satisfying about witnessing a machine
When is it important to maintain your pump?
Hydraulic pumps are a vital part of many industrial processes and are often subjected to heavy use. This means that they need to be serviced and maintained on a regular basis to ensure they are running smoothly. Here are some tips on how to keep your pump in good condition:
1. Regularly check the oil level and replace as needed. This will ensure that the pump runs smoothly and is not damaged by oil starvation.
2. Clean the exterior of the pump regularly using a stiff brush or a hose attachment capable of reaching all parts of the pump. This will remove accumulated dirt and debris, which can lead to damage or malfunctioning.
3. Inspect the seals and gaskets for wear and tear, and replace as needed. This will protect the pump from leaks and damage, and will also extend its lifespan.
What are the risks of not maintaining a pump?
Hydraulic pumps are a vital part of many industrial processes and can be expensive to replace. Maintaining a pump can help reduce the risk of it failing, and ensure that it’s functioning properly. Here are some tips for keeping your pump in good condition:
– Inspect the equipment for wear and tear regularly. This includes checking the seals, hoses, gears, shafts, and bearings. Replace anything that’s worn or damaged.
– Clean the equipment regularly using a degreaser or solvent. Remove any build-up of dirt, oil, or grease.
– Check the fluid levels and replace if necessary. Hydraulic fluid is a sensitive chemical and will degrade over time if not properly protected.
– Check for clogs and remove them using avents or fittings with built-in screens. Clean the area where the clog was found with a cleaner and solvent.

What do you need to maintain a hydraulic pump?
In order to keep a hydraulic pump running smoothly, you’ll need to make sure that the following items are always in good working order:
-Pump
-Valves
-Hoses
-Cylinder
Other Maintenance Tips for Hydraulic Pumps
Maintaining a hydraulic pump is a lot like taking care of any other mechanical equipment: regular inspections and upkeep are important to keep it running smoothly. Here are a few more tips to help keep your pump running strong:
– Inspect the seals and gaskets on the pump regularly for signs of wear or leakage. Replace them as needed.
– Regularly check the oil level in the hydraulic fluid reservoir and top off as needed. Over time, old oil can create buildup that can lead to leaks and other problems.
– Clean the hydraulic fluid filter every few months or when it starts showing signs of clogged up pores. Over time, accumulated debris can block the flow of oil and cause malfunctions.
Conclusion
Maintaining a hydraulic pump can be a daunting task, but with the right tools and techniques, it can be done successfully. By following these steps, you can ensure that your pump is running smoothly and efficiently:
1) Check the oil level regularly – When it comes to hydraulic pumps, oil is key. Make sure to check the oil level on a regular basis and add enough fresh oil if needed. This will help avoid any potential issues with the engine or system.
2) Keep an eye on the pressure – Another important aspect of maintaining a hydraulic pump is keeping an eye on the pressure levels. If they start to drop significantly, take action ASAP by cleaning or replacing parts as necessary.
3) Keep an inventory of parts – Knowing what parts are broken or missing can help you find and replace them quickly when necessary.
4) Regularly lubricate all moving parts – Lubricating all moving parts will help keep them running smoothly and prevent any damage from occurring.
How do you maintain a hydraulic pump,please click topkitparts see more